● INTRODUCTION:
Vacuum tubes are devices in which electronic conduction takes place in an evacuated glass or metal enclosure under the action of an electric field. If tha electrons are emitted from the cathode by the process of thermionic emission, the vacuum tube is referred to as the thermionic tube. A tube containing two electrodes, a cathode and an anode (also called the plate), is termed a diode. A tube having three electrodes, a cathode, a plate, and an additional electrode (called the control grid) to control the motion of the electrons within the tube, is known as a triode. The tubes with more than three electrodes are called multi-electrode tubes. Tetrodes (cotaining four electrodes), pentodes (with five electrodes), decided (having six electrodes) etc. belong to this category. In this chap
 |
| Vacuum tubes |
◆ DIRECTLY AND INDIRECTLY HEATED CATHODES :-
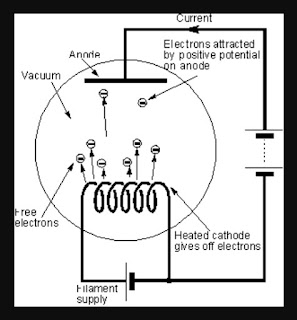
In a thermionic tube, the cathode is electrically heated to a desired temperature to obtain sufficient emission of electrons from its surface. Suitable materials for emission have been discussed. If tha heating electric current passes directly through the cathode or the filament, the cathode is termed the directly heated emitter, or directly heated cathode, or filamentary cathode. If the emitting cathode is indirectly heated by placing it in the close vicinity of a wire carrying the heating current, it is called an indirectly heated cathode.The heater wire or the filament carrying the electric current is made of tungsten or an alloy of tungsten and molybdenum. It is enclosed by a thin metal cylinder(usually of nickel), which is covered with oxide coating to serve as the indirectly heated emitter.
As the emitter material for the directly heated cathodes, thoriated tungsten is preferred to pure tungsten because it requires less power owing to its lower work function and consequently lower operating temperature.
As the emitter material for the directly heated cathodes, thoriated tungsten is preferred to pure tungsten because it requires less power owing to its lower work function and consequently lower operating temperature.
 |
| Vacuum Tube electron flow |
◆Advantages of Directly Heated Cathodes:-
The directly heated cathodes have the following advantages over the indirectly heated cathodes:-
1. As the heating element itself is the cathode, the power needed to heat the cathode is less than that for the indirectly heated cathode.
2. The electric energy dissipated in the filament is fully utilised and the desired cathode temperature is attained in a short time.
Disadvantages of Directly Heated cathodes:-
In spite of the above advantages, the filamentary cathode suffer from the following limitations which preclude their use in many vacuum tubes.
1. As the cathode is a long slender wire, the emitting surface area is small.
2. The voltage drop across the filament is sometimes comparable to the interelectrode voltages.
3.The emitting cathode is not an equipotential surface.
4. The rate of heating being proportion to the square of the current, a 100 Hz hum appears in the plate current when the filament is heated by a 50Hz alternating current. However, if a dc heating source is used, the hum is absent.
5. As the filament expands on heating, it may touch a nearby electrode. Thus filamentary cathode are not employed in the tube where the electrodes are vary closely spaced.

Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box. ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon