What is Damper winding and why it's used ?
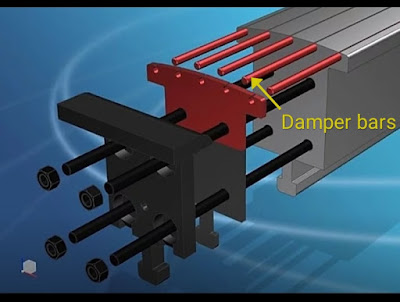
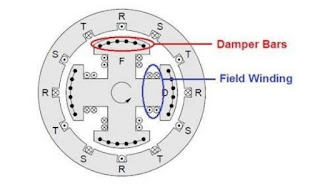
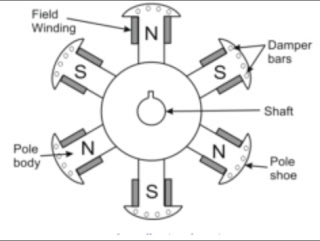
The damper winding is a special type of winding. The damper winding consists of short circuit copper bars embedded in the face of the rotor poles. The damper winding is a path for circulating of induced current when an AC supply is provided to stator of a 3-phase synchronous motor.
Stator winding produces rotating magnetic field. Due to the damper winding present in the rotor winding of the synchronous motor, machine start as a Induction motor { Induction machine works on the principle of induction.
Damper winding in synchronous motor will carry out the same track of induction motor rotor winding. Therefore due to damper winding synchronous motor start as induction motor and continue to accelerate }.
The damper winding behave in the same function as the squirrel cage of an induction machine. When rotor speed differs from the stator- side electrical speed, current are induced in the damper winding.
The current setup a torque that has the effect of pulling the rotor back toward synchronous speed. This is true with their the rotor is spinning above synchronous or below synchronous speed.
When the motor attains above 95% of the synchronous speed, the rotor winding is connected to exciter terminals and the rotor is magnetically locked by the rotating magnetic field of stator and it runs as a synchronous motor.
Function of Damper Winding :-
• Damper winding helps the synchronous motor to start on it's own by providing starting torque.
• By providing damper winding in the rotor of synchronous motor "Hunting of Machine" can be suppressed. When there is change in load, excitation or change in other conditions of the system rotor of the synchronous motor will oscillate to and for about an equilibrium position.
At times these oscillations becomes more violent and resulting in loss of synchronish of the motor and comes to halt.

Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box. ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon