What is relay ? And it's working Principle :
Definition: The relay is the device that open or closes the contacts to cause the operation of the other electric control. It detects the intolerable or undesirable condition with an assigned area and gives the commands to the circuit breaker to disconnect the affected area. Thus protects the system from damage.
All Basic Electrical Laws
Working Principle of Relay :-
 |
| Add caption |
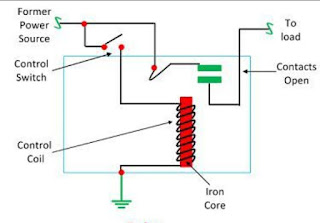
It works on the principle of an electromagnetic attraction. When the circuit of the relay senses the fault current, it energises the electromagnetic field which produces the temporary magnetic field.
 |
| Relay
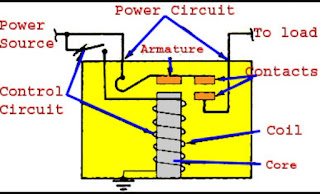
This magnetic field moves the relay armature for opening or closing the connections. The small power relay has only one contacts, and the high power relay has two contacts for opening the switch.
The inner section of the relay is shown in the figure below. It has an iron core which is wound by a control coil. The power supply is given to the coil through the contacts of the load and the control switch. The current flows through the coil produces the magnetic field around it.
Due to this magnetic field, the upper arm of the magnet attracts the lower arm. Hence close the circuit, which makes the current flow through the load. If the contact is already closed, then it moves oppositely and hence open the contacts.
Pole and Throw
The pole and throws are the configurations of the relay, where the pole is the switch, and the throw is the number of connections. The single pole, the single throw is the simplest type of relay which has only one switch and only one possible connection. Similarly, the single pole double throw relay has a one switch and two possible connections.
Construction of Relay
The relay operates both electrically and mechanically. It consists electromagnetic and sets of contacts which perform the operation of the switching. The construction of relay is mainly classified into four groups. They are the contacts, bearings, electromechanical design, terminations and housing.
Contacts – The contacts are the most important part of the relay that affects the reliability. The good contact gives limited contact resistance and reduced contact wear. The selection of the contact material depends upon the several factors like nature of the current to be interrupted, the magnitude of the current to be interrupted, frequency and voltage of operation.
Bearing – The bearing may be a single ball, multi-ball, pivot-ball and jewel bearing. The single ball bearing is used for high sensitivity and low friction. The multi-ball bearing provides low friction and greater resistance to shock.
Electromechanical design – The electromechanical design includes the design of the magnetic circuit and the mechanical attachment of core, yoke and armature. The reluctance of the magnetic path is kept minimum for making the circuit more efficient. The electromagnet is made up of soft iron, and the coil current is usually restricted to 5A and the coil voltage to 220V.
Terminations and Housing – The assembly of an armature with the magnet and the base is made with the help of spring. The spring is insulated from the armature by moulded blocks which provide dimensional stability. The fixed contacts are usually spot welded on the terminal link.
Different Types of Relays
Depending on the operating principle and structural features relays are of different types such as electromagnetic relays, thermal relays, power varied relays, multi-dimensional relays, and so on, with varied ratings, sizes and applications.
1. Electromagnetic Relays
These relays are constructed with electrical, mechanical and magnetic components, and have operating coil and mechanical contacts. Therefore, when the coil gets activated by a supply system, these mechanical contacts gets opened or closed. The type of supply can be AC or DC.
DC vs AC Relays
Both AC and DC relays work on the same principle as electromagnetic induction, but the construction is somewhat differentiated and also depends on the application for which these relays are selected. DC relays are employed with a freewheeling diode to de-energize the coil, and the AC relays uses laminated cores to prevent eddy current losses.
The very interesting aspect of an AC is that for every half cycle, the direction of the current supply changes; therefore, for every cycle the coil loses its magnetism since the zero current in every half cycle makes the relay continuously make and break the circuit. So, to prevent this – additionally one shaded coil or another electronic circuit is placed in the AC relay to provide magnetism in the zero current position.
Attraction Type Electromagnetic Relays:-
These relays can work with both AC and DC supply and attract a metal bar or a piece of metal when power is supplied to the coil. This can be a plunger being drawn towards the solenoid or an armature being attracted towards the poles of an electromagnet as shown in the figure. These relays don’t have any time delays so these are used for instantaneous operation.
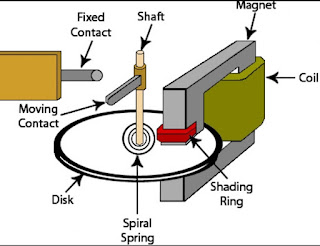
Induction Type Relays :-
These are used as protective relays in AC systems alone and are usable with DC systems. The actuating force for contacts movement is developed by a moving conductor that may be a disc or a cup, through the interaction of electromagnetic fluxes due to fault currents.
These are of several types like shaded pole, watt-hour and induction cup structures and are mostly used as directional relays in power-system protection and also for high-speed switching operation applications.
Magnetic Latching Relays
These relays use permanent magnet or parts with a high remittance to remain the armature at the same point as the coil is electrified when the coil power source is taken away.
2. Solid State Relays
Solid State uses solid state components to perform the switching operation without moving any parts. Since the control energy required is much lower compared with the output power to be controlled by this relay that results the power gain higher when compared to the electromagnetic relays. These are of different types: reed relay coupled SSR, transformer coupled SSR, photo-coupled SSR, and so on.
The above figure shows a photo coupled SSR where the control signal is applied by LED and it is detected by a photo-sensitive semiconductor device. The output form this photo detector is used to trigger the gate of TRIAC or SCR that switches the load.
3. Hybrid Relay
These relays are composed of electromagnetic relays and electronic components. Usually, the input part contains the electronic circuitry that performs rectification and the other control functions, and the output part include electromagnetic relay.
4. Thermal Relay
These relays are based on the effects of heat, which means – the rise in the ambient temperature from the limit, directs the contacts to switch from one position to other. These are mainly used in motor protection and consist of bimetallic elements like temperature sensors as well as control elements. Thermal overload relays are the best examples of these relays.
5. Reed Relay
Reed Relays consist of a pair of magnetic strips (also called as reed) that is sealed within a glass tube. This reed acts as both an armature and a contact blade. The magnetic field applied to the coil is wrapped around this tube that makes these reeds move so that switching operation is performed.
Based on dimensions, relays are differentiated as micro miniature, subminiature and miniature relays. Also, based on the construction, these relays are classified as hermetic, sealed and open type relays. Furthermore, depending on the load operating range, relays are of micro, low, intermediate and high power types.
Relays are also available with different pin configurations like 3 pin, 4 pin and 5 pin relays. The ways in which these relays are operated is shown in the belowfigure. Switching contacts can be SPST, SPDT, DPST and DPDT types. Some of the relays are normally open (NO) type and the other are normally closed (NC) types.
These are some of the different types of relays that are employed in most of the electronic as well as electrical circuits. The information about the different types of relays serves readers’ purpose and we hope that they will find this basic information very useful. Considering the huge significance of relays with zvs in circuits, this particular article on them deserves its readers’ feedback, queries, suggestions and comments. Therefore, readers can post their comments here.
|




Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box. ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon