What is Synchronous Motor ?
Introduction :-
The motor which runs at synchronous speed is known as the synchronous motor. The synchronous speed is the constant speed at which motor generates the electromotive force. The synchronous motor is used for converting the electrical energy into mechanical energy.
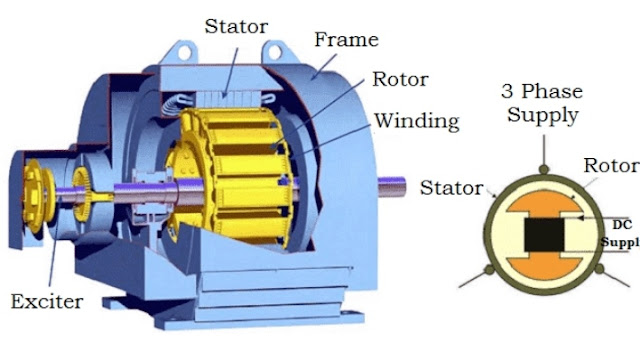
Construction of synchronous motor :-
The stator and the rotor are the two main parts of the synchronous motor. The stator becomes stationery, and it carries the armature winding of the motor. The armature winding is the main winding because of which the emf induces in the motor. The rotor carry the field winding. The main field flux induces in the rotor. The rotor is designed in two ways, i.e. the salient pole rotor and non-salient pole rotor.
Salient pole Rotor:
In salient pole type of rotor consist of large number of projected pole (salient pole) mounted on a magmatic wheel. The projected poles are made up from laminated of steel. The lamination reduce the eddy current loss occurs on the winding of the transformer. For obtaining the high-speed rotor is used in the motor. The rotor winding is provided on these poles and it is supported by pole shoes. Salient pole rotors generally need damper winding to prevent rotor oscillations during operation.
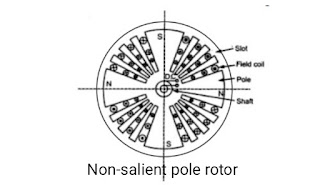
Non-salient pole (cylindrical) rotor :-
Non-salient pole rotors are cylindrical in shape having parallel slots on it to place rotor winding. It is made up of solid steel. It is have small in diameter but having longer axial length. Damper winding are not need in non-salient poles rotors.
Synchronous motor working principle :-
The stator and rotor are the two main parts, and the rotor is the rotating part of the motor. The stator contains 3-phase winding and 3-phase AC supply is given to the stator of the motor. The stator and rotor both are excited separately. Thus excitation produce 3-phase rotating magnetic field on the parts of the motor with the help of an electric current.
When the 3-phase AC supply is given to the stator, the rotating magnetic field developed between the stator and rotor gap. The field having moving polarities is known as the rotating magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field develops only in the polyphase system. Because of the rotating magnetic field, the north and south poles develop on the stator.
The rotor is excited by the DC supply. The DC supply induces the north and south poles on the rotor. As the DC supply remains constant. Thus the flux has fixed polarity. The north pole developed on one end of the rotor and the south pole develops on outher end.
Speed of the synchronous motor is controlled by the frequency of the applied AC supply. The AC is sinusoidal. The polarity of the wave change in every half cycle,i.e. the wave remains positive in the first half cycle and became negative in the second half cycle. The position and negative half cycle of the wave develops the north and south pole on the stator respectively.
When the rotor and stator both have the same pole on the same side, they repel each other. If they opposite pole, they attract each other. This can easily be understood with the help of the figures shown below.
The rotor attracts towards the pole of the stator for the first half cycle of the supply and repulse for the second half cycle. Thus the rotor becomes pulsates only at one place. This is the reason because of which the synchronous motor is not self-starter.
The prime mover is used for rotating the motor. The prime mover rotates the rotor at their synchronous speed. The synchronous speed is the constant speed of the machine whose value depends on the frequency and the noumbers of the pole of the machine.
When the rotor starts rotating at their synchronous speed, the prime mover is disconnected to the motor. And the DC supply is provided to the rotor because of which the north and south pole develops at their ends.
The north and south poles of the rotor and the stator interlock each other. Thus, the rotor starts rotating at the speed of the rotating magnetic field. And the motor runs at the synchronous speed. The speed of the motor can only be changed by changing the frequency of the supply.
When the rotor and stator both have the same pole on the same side, they repel each other. If they opposite pole, they attract each other. This can easily be understood with the help of the figures shown below.
 |
| Synchronous motor |
The rotor attracts towards the pole of the stator for the first half cycle of the supply and repulse for the second half cycle. Thus the rotor becomes pulsates only at one place. This is the reason because of which the synchronous motor is not self-starter.
The prime mover is used for rotating the motor. The prime mover rotates the rotor at their synchronous speed. The synchronous speed is the constant speed of the machine whose value depends on the frequency and the noumbers of the pole of the machine.
When the rotor starts rotating at their synchronous speed, the prime mover is disconnected to the motor. And the DC supply is provided to the rotor because of which the north and south pole develops at their ends.
The north and south poles of the rotor and the stator interlock each other. Thus, the rotor starts rotating at the speed of the rotating magnetic field. And the motor runs at the synchronous speed. The speed of the motor can only be changed by changing the frequency of the supply.




1 comments:
Click here for commentsNice atical 😊😊😊🤗
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box. ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon