The electric fuse works on which phenomenon ?
Fuse is the most essential part of the power system its protect the all industrial and house hold application from High voltage and short-circuit.
Definition: A fuse is a short piece of metal, inserted in the circuit, which melts when excessive current flows through it and thus breaks the circuit.The fuse element is generally made of materials having low melting point, high conductivity and least deterioration due to oxidation e.g., silver, copper etc. It is inserted in series with the circuit to be protected. Under normal operating conditions, the fuse element is at a temperature below its melting point.
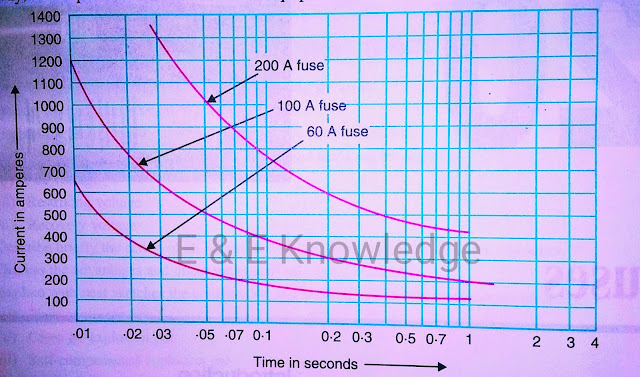 |
| Inverse time-current characteristics |
Therefore, it carries the normal current without overheating. However, when a short-circuit or overload occurs, the current through the fuse increases beyond its rated value. This raises the temperature and fuse element melts, disconnecting the circuit protected by it. In the way, a fuse protects the machines and equipment from damage due to excessive currents.
The time required to blow out the fuse depends upon the magnitude of excessive current. The greater the current, the smaller is the time taken by the fuse to blow out. In other words, a fuse has inverse time-current characteristics
Such a characteristic permits its use for overcurrent protection.
Characteristics of Fuse Element :
The function of a fuse is to carry the normal current without overheating but when the current exceeds its normal value, it rapidly heats up to melting point and disconnects the circuit protected by it. In order that it may perform this function satisfactorily, the fuse element should have the following desirable characteristics :
- Low melting point e.g., tin, lead.
- High conductivity e.g., silver, copper.
- Free from deterioration due to oxidation e.g., silver.
- Low cost e.g., lead, tin, copper.
The above discussion reveals that no material possesses all the characteristics. For instance, lead has low melting point but it has high specific resistance and is liable to oxidation. Similarly, copper has high conductivity and low cost but oxidised rapidly. Therefore, a compromise is made in the selection of material for a fuse.


Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box. ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon