What is power factor ?
The cosine of angle between voltage and current in an a.c. circuit is known as power factor.
In an a.c. circuit, there is generally a phase difference ø between voltage and current. The term cos ø is called the power factor of the circuit. If the circuit is inductive, the current lags behind the voltage and the power factor is referred to as lagging. However, in a capacitive circuit, current leads the voltage and Power factor is said to be leading.
Consider an inductive circuit taking a lagging current I from supply voltage V; the angle of lag behind ø. The phasor diagram of the circuit is shown below
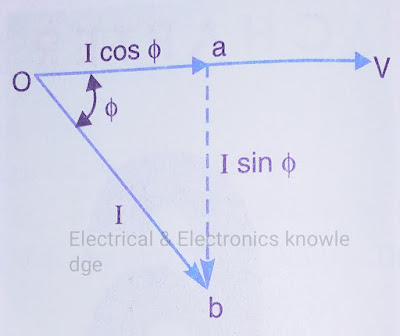 |
| Phasor diagram of power factor |
The circuit current I can be resolved into two perpendicular components, namely;
- I cos ø in phase with V
- I sin ø 90° out of phase with V
The component I cos ø is known as active or wattful component,
whereas compo I sin ø is called the reactive or wattless component.
The reactive component is a measure of the power factor. If the reactive component is small, the phase angle ø is small and hence power factor cos ø will be high. Therefore, a circuit having small reactive current (i.e., I sin ø) will have high power factor and vice-versa. It may be noted that value of power factor can never be more than unity.
- It is a usual practice to attach the word ‘lagging’ or ‘leading' with the numerical value of power factor to signify whether the current lags or leads the voltage. Thus if the circuit has a p.f.of 0.5 and the current lags the voltage, we generally write p.f. as 0.5 lagging.
- Sometimes power factor is expressed as a percentage. Thus 0.8 lagging power factor may be expressed as 80% lagging.

Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box. ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon